Autism Therapy
There are many types of autism therapy that can help your child overcome their symptoms of autism and live a normal and healthy life. The following are some of the therapies and autism programs that are being conducted by our experts at FIT-IN.
Early Intervention Program (EIP)
Early Intervention Programs (EIP) are used to recognize any issues or delay in your child’s development. This program focuses on early identification and detailed assessments towards the children’s needs. Through a series of tests and filters, our trained experts will be able to diagnose if your child has any developmental issues.
The program is custom tailored to the needs and suitability of the child, along with ensuring that the parents are given proper education and guidance on the best practices for their child’s development. EIP usually consists of a combination of the following therapies and programs:
ABA Therapy
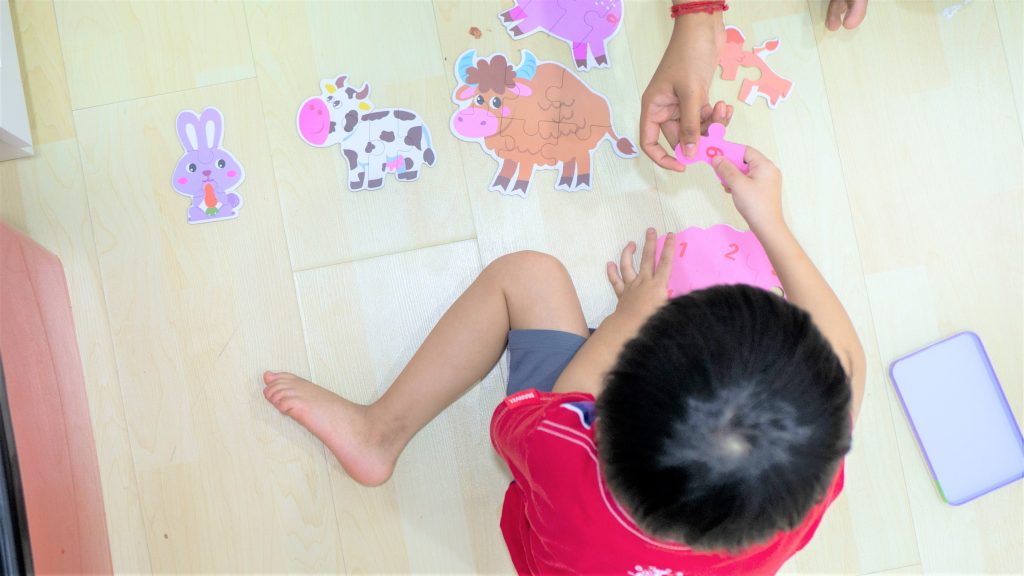

Applied Behavioral Analysis (ABA) Therapy is the optimum treatment for children with autism to improve their social, communication and learning skills. This gold standard practice focuses on the understanding and the changing of an individuals behavior, specifically children on the autism spectrum or those who have learning disabilities.
This type of therapy focuses on the concept that wanted behavior can be trained through positive reinforcement. It also involves learning at different levels, where different skills are introduced step by step following the child’s ability.
Occupational Therapy
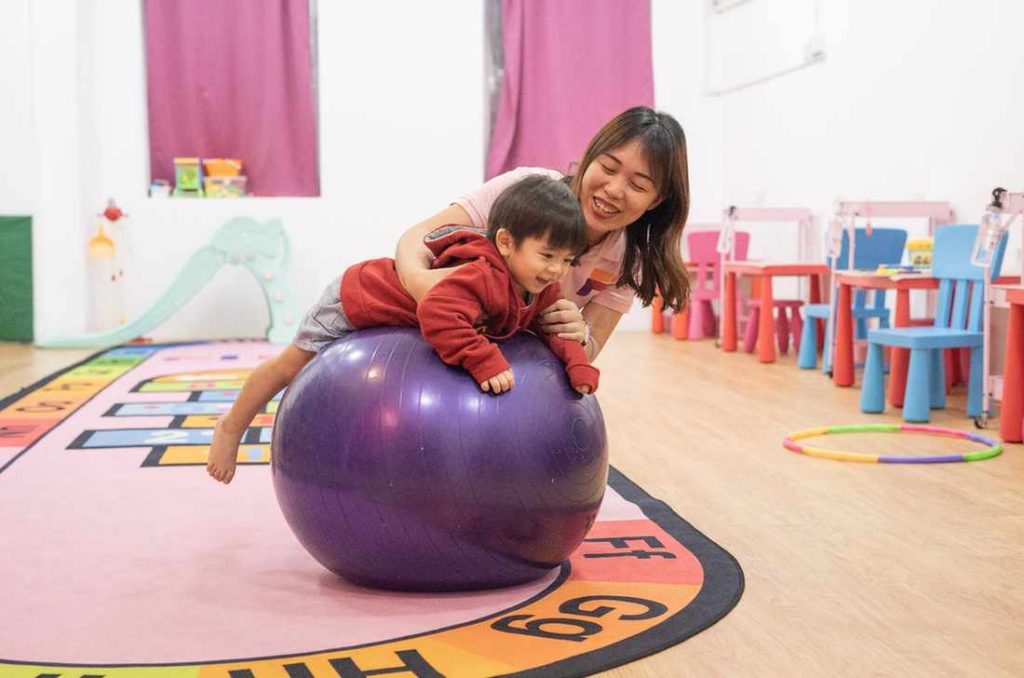

Occupational Therapy (OT) aims to help teach and improve the skills required for children to function better in their daily lives. For children with special needs, such as autism or learning disabilities, our therapy is able to help them obtain, fix and maintain their skills used daily. Occupational therapy usually focus on a few aspects such as:
- Motor-sensory skills: It helps children understand and control their sensory inputs (smell, touch and sound) along with improving their motor skills (writing, holding small items).
- Self care: Skills used daily such as showering, wearing clothes, eating and self hygiene.
- Cognitive skills: Helping children fix their focus, memory and problem solving skills.
- Social skills: Teaches children social cues, how to respond to others and how to interact more effectively.
The involvement of children in occupational therapy helps to overcome the challenges faced in their daily lives. Our therapists use different methods such as play activities, sensory techniques and therapeutic strategies to help your child reach their development goals.
Sensory Therapy

Sensory therapy, also known as sensory integration therapy is a method used to help children handle and control their sensory inputs (such as touch, sound, smell, and light) which they might process excessively or not as strongly as everyone else.
At FIT-IN, sensory therapy aims to help children in:
- Handling and controlling sensitivities: Children with autism frequently feel their sensory inputs more intensively. Our therapy helps them recognize, handle and interact with their senses without them being affected or overstimulated.
- Improving their sensory experience: For children with lesser response towards sensory input, we try to improve their sensitivity towards their senses.
- Improve their adapting skills: We also teach the children how to adapt to their surroundings and how to control their senses better.
Our sensory therapy involves different activities and exercises which are designed to increase or reduce sensory responses, depending on the needs of the child. As a reminder, this therapy is a very personal method that has to be amended to fit the child’s needs. With this therapy, they are able to understand and control their senses, to improve their daily lives and social activities.
Speech Therapy
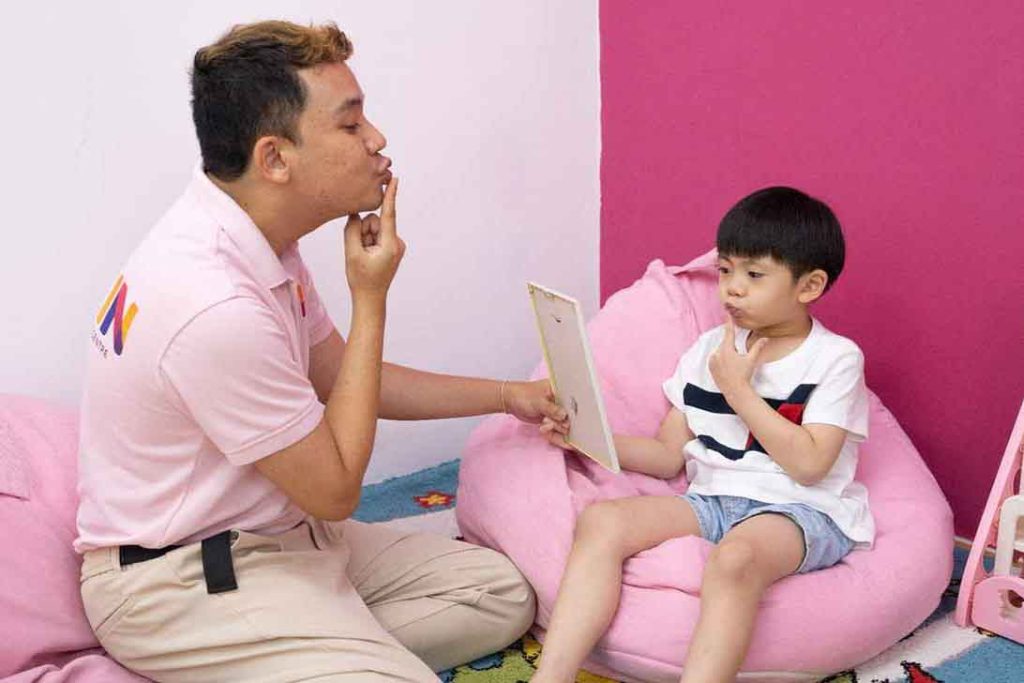

Speech therapy focuses on the improvement of speech, language and communication with others. At FIT-IN, our therapy aims to improve:
- Communication skills: By helping children expand and fix their language and speech skills, through learning new vocabulary, sentences and the correct use of phrases/sentences in different situations.
- Social cues: Help the children understand different social cues and contexts, reading facial expressions and how to interact with other people.
Our speech therapy involves many activities and exercises prepared to help children use language more effectively. Our therapists also will work together with the children’s family to discuss effective teaching strategies for their child’s needs, along with being given training and guidance on how to develop their child’s language and speech at home.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Can ABA Therapy help with repetitive behavior and meltdowns that my child faces?
- Yes, it can help by replacing the unwanted behaviors with functional behaviors and teaching them alternative responses through positive reinforcement.
- How can ABA Therapy be customized to the needs and learning style of my child?
- It is designed to be customized to each individual, our therapists will identify the best ways to educate your children based on their ability and their interests.
- How can sensory therapy help my child improve their focus in school or at home?
- It helps by teaching your child how to understand and process their stimulus that they are receiving, and to channel their focus to the task at hand in different environments.
- What are some early signs of developmental issues that I should be aware of?
- Some early signs are not speaking at the expected ages, difficulty in understanding instructions, or a lack of interest in words/speaking.
- What are some fun and interesting activities that I can do at home to train my child’s speech and language?
- Reading together, having speaking games, or trying to engage in conversation daily to help stimulate and improve your child’s speech and language skills.
- How can occupational therapy help with improving skills?
- It can help via specially planned activities that help fix fine motor skills, such as holding pencils or manipulating small objects.
-
 Book Assessment
Book Assessment