Behaviour Therapy For Children
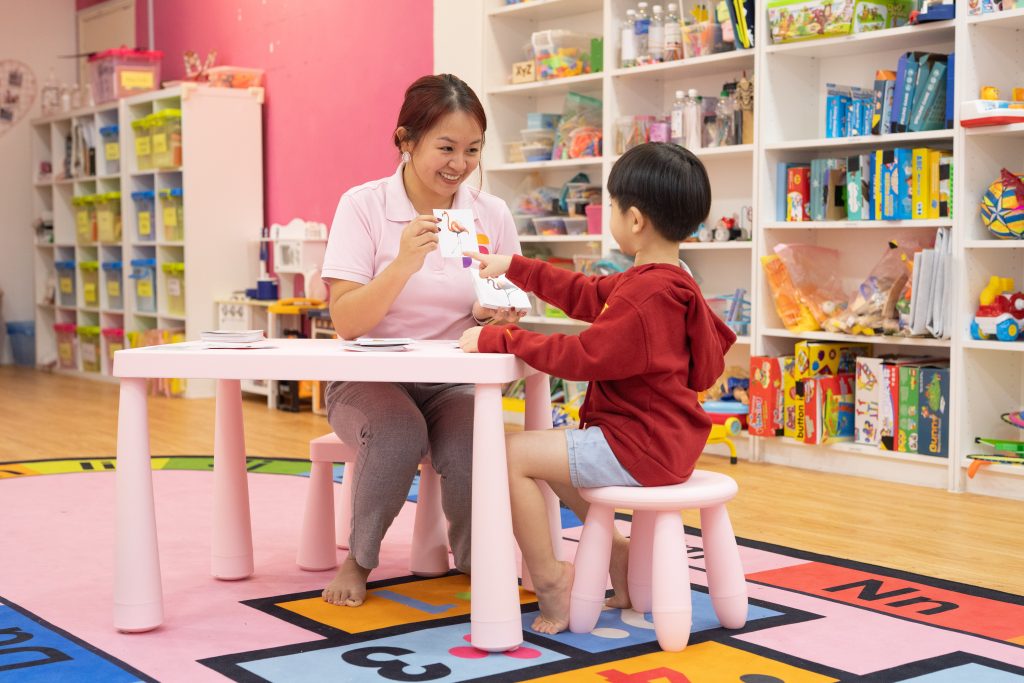

Behaviour therapy, also known as applied behaviour analysis (ABA) therapy is a form of therapy that is a valuable intervention aimed at addressing specific behaviors, fostering social skills, and enhancing overall quality of life for children with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD).
There are a few approaches commonly used in behaviour therapy, which are :
- Positive Behavioural Support (PBS). PBS aims to figure out why a child does a particular problem behavior. It works to change the environment, teach skills, and make other changes that make a correct behavior more positive for the child. This encourages the child to behave more appropriately.
- Pivotal Response Training (PRT). PRT takes place in the child’s everyday environment. Its goal is to improve a few “pivotal” skills, such as motivation and taking initiative to communicate. These help the child to learn many other skills and deal with many situations.
- Early Intensive Behavioural Intervention (EIBI). EIBI provides individualized, behavioural instruction to very young children with ASD. It requires a large time commitment and provides one-on-one or small-group instruction.
- Discrete Trial Teaching (DTT). DTT teaches skills in a controlled, step-by-step way. The teacher uses positive feedback to encourage the child to use new skills.
Key Principles of Behaviour Therapy:
- Individualized Approach:
- Every child with autism is unique, and behaviour therapy recognizes the importance of tailoring interventions to meet the specific needs and preferences of each child. Therapists work closely with families to understand the child’s strengths, challenges, and goals.
- Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA):
- ABA is a widely used and evidence-based approach in behaviour therapy for autism. It involves breaking down complex behaviors into smaller components, analyzing patterns, and implementing strategies to reinforce positive behaviours while reducing challenging ones.
- Functional Behavior Assessment (FBA):
- Conducting an FBA helps therapists identify the underlying reasons for specific behaviours. By understanding the function of behavior, therapists can design interventions that target the root causes, promoting more effective and lasting change.
- Positive Reinforcement:
- Positive reinforcement involves rewarding desired behaviours to encourage their repetition. This could include praise, tokens, or other incentives that motivate the child. By focusing on positive reinforcement, behavior therapy aims to build a repertoire of socially appropriate behaviors.
- Social Skills Training:
- Many children with autism struggle with social interactions. Behavior therapy incorporates social skills training to help children understand and navigate social cues, develop friendships, and engage in meaningful communication with peers and adults.
- Visual Supports:
- Visual supports, such as visual schedules and cues, are commonly used in behavior therapy to enhance communication and comprehension. Visual aids provide a structured and predictable environment, reducing anxiety and promoting successful task completion.
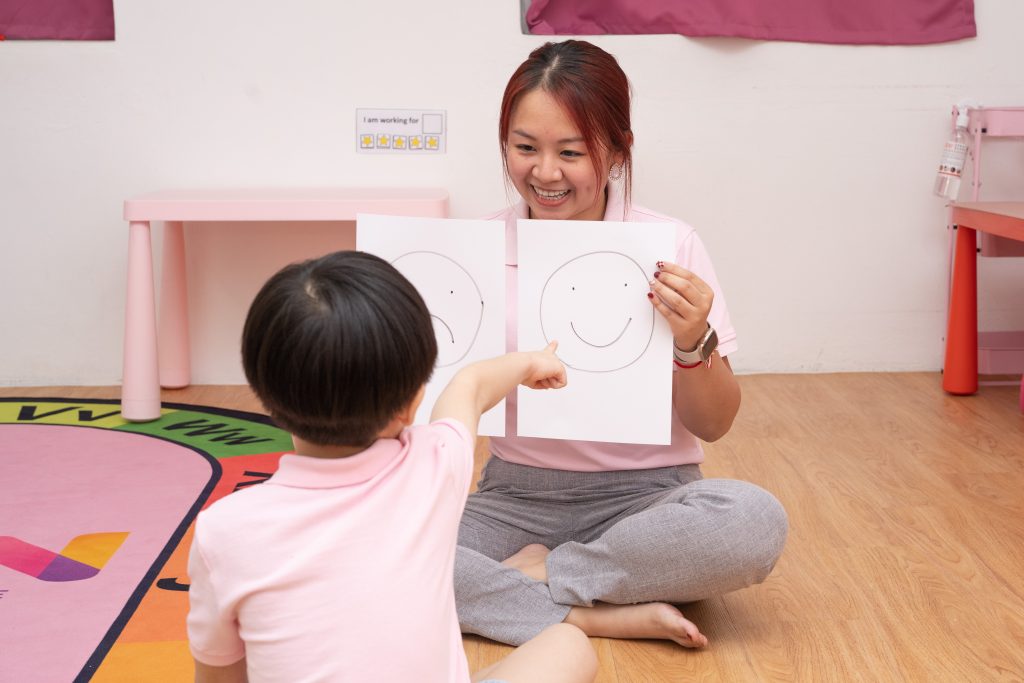

Benefits of Behaviour Therapy:
- Improved Communication:
- Behaviour therapy often includes strategies to enhance communication skills, whether through verbal language, sign language, or alternative communication methods. This can empower children to express their needs, thoughts, and feelings more effectively.
- Enhanced Social Interactions:
- Social skills training fosters meaningful connections with others. Autistic children learn how to initiate conversations, interpret social cues, and engage in cooperative play, contributing to improved social interactions.
- Reduced Challenging Behaviours:
- Targeting challenging behaviours through ABA and positive reinforcement can lead to a significant reduction in behaviors that may interfere with daily activities and social relationships.
- Increased Independence:
- By addressing specific challenges and building essential skills, behavior therapy aims to promote independence in daily living activities, self-care, and decision-making.
FAQ
- What is Applied Behaviour Analysis (ABA), and why is it commonly used in behaviour therapy for autism?
- ABA is a therapeutic approach that breaks down behaviors into smaller components, analyzes patterns, and uses positive reinforcement to encourage desired behaviors. It is evidence-based and widely used in autism intervention due to its effectiveness in promoting behavioral change.
- How long does behaviour therapy typically last?
- The duration of behaviour therapy varies based on the individual needs and progress of the child. Some children may benefit from shorter-term interventions, while others may require ongoing support.
- Can behaviour therapy be adapted to suit my child’s unique needs and preferences?
- Yes, behaviour therapy is individualized to meet the specific needs, strengths, and preferences of each child. Our therapists will work closely with families to tailor interventions and ensure they are effective and comfortable for the child.
- What specific behaviours can behaviour therapy address in my child?
- Behaviour therapy can address a range of behaviours, including communication challenges, repetitive behaviours, social difficulties, tantrums, and aggression. The focus is on reinforcing positive behaviours and reducing behaviours that may interfere with daily life.
- How can I support my child’s progress at home during and after behaviour therapy sessions?
- Our therapists will provide guidance and strategies for parents to reinforce learned skills at home. Consistency in implementing these strategies, providing positive reinforcement, and creating a structured environment can support the child’s progress.
- Are there potential side effects or downsides to behaviour therapy?
- Behaviour therapy is generally safe and well-tolerated. However, it’s crucial to communicate openly with the therapist about any concerns or observations. The therapist can adjust the intervention plan if needed.
- Will my child always need behaviour therapy, or can they eventually “graduate” from it?
- The duration of behaviour therapy varies for each child. Some may benefit significantly and require less intensive support over time, while others may benefit from ongoing interventions. The goal is to promote independence and positive behaviors.
- How do I know if behaviour therapy is the right choice for my child?
- Behaviour therapy is often recommended for children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) to target specific behaviors and improve social and communication skills. Contact our team of professionals to determine the suitability for your child.
Contact Us
Cyberjaya
FR-02-08 & FR-03-08, Tamarind Suites,
Persiaran Multimedia, Cyber 10,
63000 Cyberjaya, Selangor
+6 018-388 3590
Senior Centre Manager – Mr Shafiq
+60 11-1153 6388
Therapist – Mr Hong
Bukit Jelutong
No 7-1, Jalan Ungu B U9/B,
Sunway Kayangan, Section, U9,
40150 Shah Alam, Selangor
+60 18-664 6074
Centre Manager – Ms Yee
+60 11-1152 6074
Assistant Manager – Ms Anis
Bandar Menjalara, KL
59-1 Jalan Medan Putra 1,
Medan Putra Business Centre,
52200 Kepong, Kuala Lumpur
+60 11-1153 6388
Senior Centre Manager – Mr Chu
+60 11-1152 6074
Assistant Manager – Ms Anis
Eco Majestic, Semenyih
12A-2, Jalan Eco Majestic 10/1D,
Eco Majestic, 43500 Semenyih,
Selangor
+60 11-1138 8359
Centre Manager – Mr Zan
+60 11-1168 6074
Senior Therapist – Ms Adda
Eco Santuari, Telok Panglima Garang
2A-1, Jalan Eco Sanctuary 8/1A,
Eco Santuari, 42500 Telok Panglima Garang,
Kuala Langat, Selangor
+60 11-1168 6074
Senior Therapist – Ms Adda
+60 11-1153 6388
Therapist – Mr Hong
 Book Assessment
Book Assessment